5 Best GIS Tools for Better Geospatial Mapping
Geospatial mapping tools are important for visualizing data, whether mapping pipeline infrastructure or managing field inspections. Yet, with many available platforms, it can be tough to determine which geographic information system (GIS) tool best fits project scope, budget and technical needs.
Some tools excel in computer-aided design (CAD) integration, while others are better for mobile field data collection. To make a more informed decision, professionals can understand the following GIS tools to power smarter geospatial mapping.
1. TRC Companies Lemur
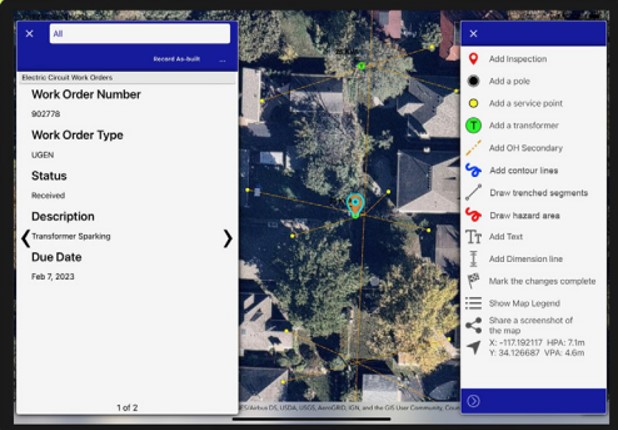
Source: https://www.trccompanies.com/products/lemur/
Lemur by TRC Companies is a field data collection platform that combines GIS mapping, custom digital forms and real-time field-to-office data syncing. It is an all-in-one solution, providing a streamlined way to capture and update geospatial data directly from the field.
For teams managing critical infrastructure, working in remote locations is common. Lemur ensures field crews can continue working anywhere with its offline capabilities. Once reconnected, data automatically syncs with the central systems, reducing delays and improving accuracy. This platform also supports barcode scanning, photo capture and customizable workflows, which allows it to manage a wide range of assets.
Lemur facilitates higher-quality data, workflow efficiency and digital transformation. With a practical and adaptable GIS tool like this, energy and utility organizations can seamlessly enhance broader intelligent grid and infrastructure initiatives.
2. Esri ArcGIS
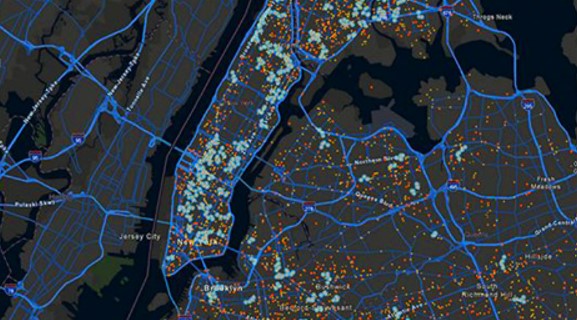
Source: https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/geospatial-platform/overview
ArcGIS by Esri supports everything from detailed mapping and spatial analysis to field data collection and real-time monitoring. For field crews, it offers a flexible system capable of handling complex infrastructure, regulatory requirements and environmental considerations in one place.
ArcGIS is also scalable. Whether a team is mapping thousands of miles of pipeline or monitoring asset conditions across remote sites, the platform can grow with their needs.
This GIS tool also features analytics and data visualization. It lets users layer live data, historical patterns and predictive modeling to better understand how their assets perform across geographic regions and time frames. It’s powerful and efficient in building workflows and centralizing but may require some training to get the most out of it.
3. QGIS
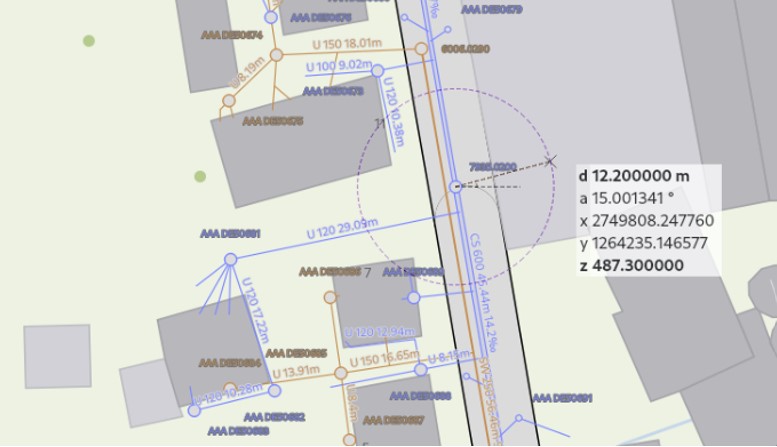
Source: https://qgis.org/
QGIS is an open-source alternative that delivers a surprising amount of power and flexibility without the licensing costs of enterprise platforms. It can be a cost-effective way to manage and visualize spatial data for those working on leaner budgets or exploratory projects.
Despite being open source, QGIS supports geospatial formats and has a large ecosystem of plug-ins. Whether mapping pipeline routes or overlaying land use data, QGIS is configurable to fit users’ needs. It works well alongside other tools — like PostGIS and GRASS GIS — and mobile data collection apps like QField.
4. Caliper Maptitude
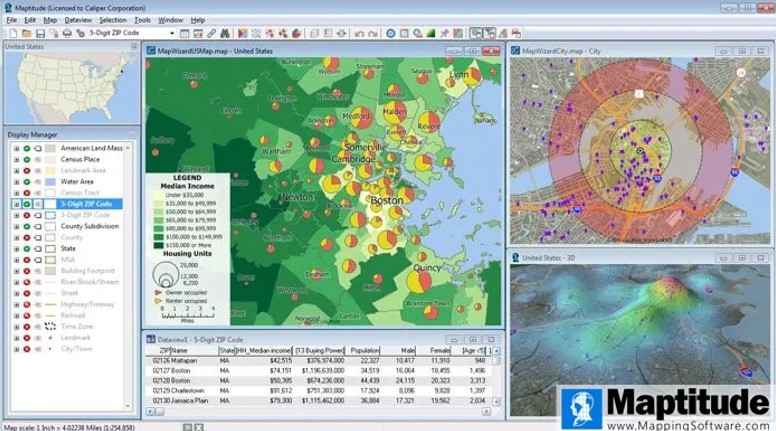
Source: https://www.caliper.com/maptitude/mapping-software.htm
Maptitude by Caliper is a GIS and mapping software that offers accessibility and usability. While its strengths lie in demographic and business analysis, it also holds value for field crews who need to visualize infrastructure, analyze service areas or plan site development.
A vast library of preloaded data — including demographics, transportation networks and land use maps — helps teams quickly generate insights without sourcing or integrating third-party datasets. For example, Maptitude makes it easy to visualize spatial relationships from the start when planning pipeline expansions.
It also supports GPS integration and custom overlays, letting users tailor maps to their operational goals. While Maptitude may offer the same advanced modeling tools as ArcGIS, its approachable interface and strong data visualization make it a good choice for fast, clear mapping.
5. Autodesk AutoCAD Map 3D
Source: https://www.autodesk.com/products/autocad/included-toolsets/autocad-map-3d
AutoCAD Map 3D by Autodesk offers traditional CAD design with geospatial data management. It allows users to create, edit and analyze spatially accurate designs while tying them to real-world geographic context.
One of its biggest advantages is integrating enterprise systems and spatial databases. This enables engineers and planners to collaborate more effectively, using consistent data formats and workflows.
AutoCAD Map 3D also provides precision tools. Its geospatial analysis capabilities can identify risks and optimize routes. While it’s not a replacement for a full GIS suite, AutoCAD Map 3D adds strong spatial intelligence to engineering-driven projects.
What Is the Best GIS Tool?
Determining the best GIS tool depends on a company’s needs. Some teams may prioritize real-time data syncing and field-ready features, while others need seamless integration or cost-effective customization.
Each tool in this guide has its own strengths that help with different geospatial mapping projects. Considering the team’s goals and how these GIS tools fit within the existing infrastructure can lay the foundation for choosing the right platform.
